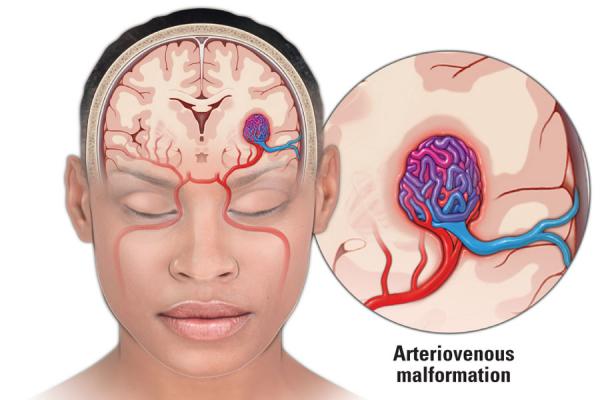
An arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is a jumble of arteries and veins with no capillaries between them. This can happen in your brain or other areas. An AVM can cause bleeding or damage to tissues around it. Some people don’t have symptoms until an AVM starts to bleed. Treatments can remove an AVM, shrink it or stop blood from flowing through it. Symptoms of AVM include;
Headache, Numbness or tingling sensation, Dizziness, Problems with movement, speech, memory, thinking, balance or vision.
How does an arteriovenous malformation affect my body?
AVMs cause harm in the following ways
Bleeding: The force of the blood flow from your arteries brings a lot of pressure to the AVM.
Veins have weak walls and can’t always adjust to the pressure of blood flow.
Pressing on body parts: An abnormal connection results in more blood in your veins. Veins can get big and press on nearby tissue. This not only prevents oxygenation, but also impacts draining through your lymphatic system.
Depleting tissues of needed oxygen, Because there’s no capillary bridge between arteries and veins, oxygen and nutrients don’t get to the tissue where there’s an AVM. The tissue and nerve cells at that site can die.
Coma and death, especially from a large bleed in your brain.
And finally, Get medical care right away if you notice any symptoms of a brain AVM, such as seizures, headaches or other symptoms. A bleeding brain AVM is dangerous and requires emergency medical care. Always contact your Healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment. All these information are gotten from Cleveland Clinic.