Scientists have discovered what they say is the smallest known dinosaur.
The new species has been described by one team member as the “weirdest fossil” she has ever worked on.
The specimen, from northern Myanmar, consists of a bird-like skull trapped in 99-million-year-old amber.
Writing in the prestigious journal Nature, researchers report that the dinosaur would have been similar in size to the bee hummingbird – the tiniest living bird.
The stunning find may shed light on how small birds evolved from dinosaurs – which were often bigger.
While the smallest dinosaurs, such as the bird-like Microraptor, weighed hundreds of grams, the bee hummingbird weighs just 2g.
“Animals that become very small have to deal with specific problems, like how to fit all sensory organs into a very small head, or how to maintain body heat,” said Prof Jingmai O’Connor from the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Beijing.
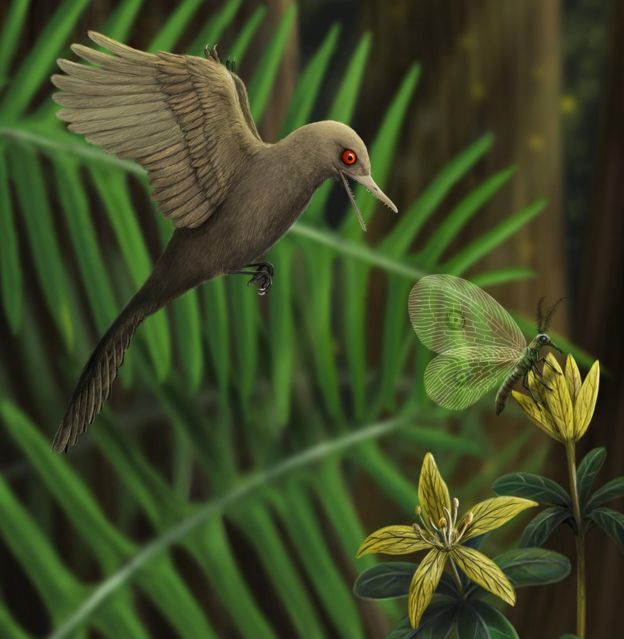

The new species, dubbed Oculudentavis khaungraae, appears to have dealt with these challenges in unusual ways.
For example, the animal’s eye structure surprised the scientists.
Birds have a ring of bones, the scleral ring, that helps to support the eye. In most birds, the individual bones, called scleral ossicles, are simple and fairly square.
But in Oculudentavis, they are spoon-shaped, a characteristic previously only found in some living lizards.
The bones of the eye would have formed a cone, like the eye bones in owls. This indicates that the dinosaur had exceptional vision.
Unlike owls, the eyes faced sideways and the opening at the centre of the ossicles was narrow, which would have restricted the amount of light coming into the eye. This provides strong evidence that Oculudentavis was active in the daytime.
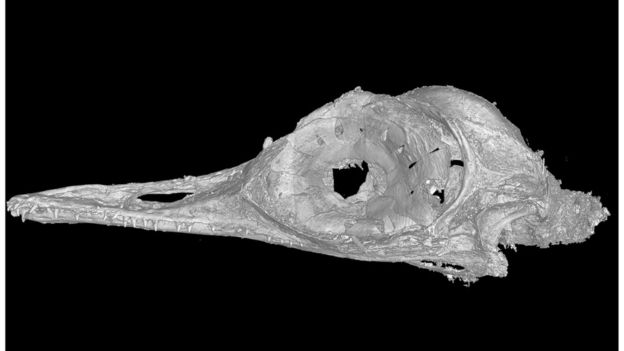
In addition, the creature’s eyes would have bulged out of its head in a manner not seen in any other living animal, making it hard to understand exactly how the eyes functioned.
“It’s the weirdest fossil I’ve ever been lucky enough to study,” Prof O’Connor explained. “I just love how natural selection ends up producing such bizarre forms. We are also super lucky this fossil survived to be discovered 99 million years later.”
Because the new specimen consists of only a skull, understanding how it is related to birds is unclear. Some features of the skull are like those of dinosaurs, while others are like those of very advanced birds.
The researchers say that the new specimen’s remarkable suite of traits could have evolved either through the constraints of miniaturisation, or through becoming specialised to a particular lifestyle.
The dinosaur’s jaw had a surprisingly large number of teeth. This would appear to suggest that, despite its tiny size, Oculudentavis was a predator that ate insects.



